Variations in Nutritional Content

Cheese pizza nutrition facts – The nutritional content of cheese pizza can vary significantly depending on several factors, including crust type, cheese quantity, and the addition of toppings. Understanding these variations is crucial for making informed dietary choices. This section will explore the impact of these factors on the overall nutritional profile of a cheese pizza.
Crust Type: Thin Crust vs. Deep Dish
The type of crust significantly influences the caloric and macronutrient content of a cheese pizza. Deep-dish pizzas generally contain more calories and carbohydrates due to their thicker crust and higher volume. Thin-crust pizzas, conversely, tend to be lower in calories and carbohydrates, offering a potentially healthier alternative. The following table provides a comparison, based on average values for a single serving (approximately 1/8 of a 14-inch pizza):
| Nutrient | Thin Crust Cheese Pizza | Deep Dish Cheese Pizza |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 250-300 | 350-450 |
| Total Fat (g) | 10-12 | 15-20 |
| Saturated Fat (g) | 5-7 | 8-12 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 30-35 | 45-55 |
| Protein (g) | 10-12 | 12-15 |
| Sodium (mg) | 600-800 | 700-900 |
*Note: These values are estimates and can vary widely depending on the specific recipe and ingredients used.*
Cheese Quantity and Nutritional Profile, Cheese pizza nutrition facts
The amount of cheese significantly impacts the fat and calorie content of a pizza. Increasing the cheese quantity proportionally increases the fat, saturated fat, and calorie count. For example, a pizza with double the cheese will approximately double the fat and calorie content compared to a pizza with a standard amount of cheese. This is primarily due to the high fat content of cheese, particularly saturated fat which is associated with increased cholesterol levels.
Reducing the amount of cheese can help lower the overall fat and calorie intake.
Impact of Toppings on Nutritional Value
Adding toppings to a cheese pizza can alter its nutritional profile, either positively or negatively. Vegetable toppings, such as peppers, onions, and mushrooms, generally add fiber and micronutrients without significantly increasing the calorie or fat content. However, meat toppings, like pepperoni or sausage, substantially increase the fat, saturated fat, sodium, and calorie content. For instance, adding pepperoni can increase the calorie count by 100-150 calories per serving, while adding vegetables might only add 20-30 calories.
The choice of toppings therefore plays a significant role in determining the overall nutritional value of the pizza.
Health Implications and Considerations
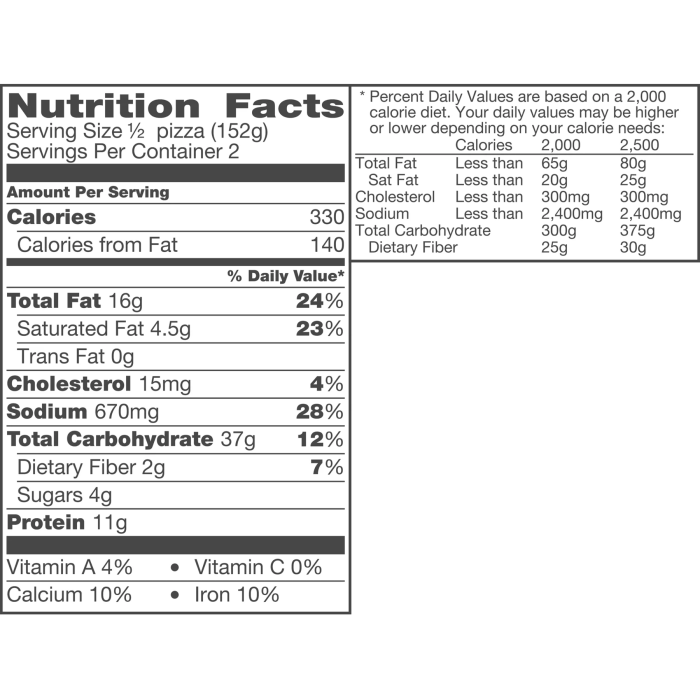
Regular consumption of cheese pizza, while enjoyable, presents potential health risks due to its high caloric density and concentration of certain nutrients. Understanding these risks and how to mitigate them is crucial for incorporating pizza into a balanced diet. Excessive intake can contribute to weight gain, increased cholesterol levels, and other health concerns.Cheese pizza, primarily due to its cheese and processed meat components (if added), is often high in saturated fat and sodium.
Saturated fat contributes to elevated cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease. High sodium intake is linked to hypertension (high blood pressure), a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease and stroke. Furthermore, the refined grains typically used in pizza crust contribute to a high glycemic index, leading to potential blood sugar spikes. However, these risks can be significantly reduced through mindful portion control and mindful choices regarding toppings and frequency of consumption.
Cheese Pizza and Balanced Diets
Cheese pizza can be incorporated into a balanced diet as an occasional treat, rather than a staple food. Moderation is key. A single slice of cheese pizza, as part of a larger meal plan that emphasizes fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, will not significantly detract from overall nutritional balance. Prioritizing nutrient-dense foods throughout the week allows for occasional indulgences like pizza without jeopardizing long-term health.
Cheese pizza, a beloved comfort food, often boasts high fat and calorie counts. Understanding the nutritional breakdown is crucial for mindful eating, and comparing it to lighter alternatives is key. For instance, you might consider the lower-calorie option of babybel cheese nutrition light as a potential snack. Returning to pizza, opting for thin crust and lean toppings can help manage overall cheese pizza nutrition facts.
The nutritional value of a single slice can be enhanced by opting for whole-wheat crust and adding vegetables like mushrooms or peppers.
Sample Meal Plan Incorporating Cheese Pizza
The following sample meal plan demonstrates how to include a slice of cheese pizza while maintaining a balanced nutritional intake. This plan is a suggestion and individual needs may vary. Calorie needs and macronutrient ratios should be adjusted based on individual factors like age, activity level, and health goals.
| Meal | Food | Approximate Nutritional Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with berries and nuts | High in fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats |
| Lunch | Large salad with grilled chicken or fish, mixed greens, and a light vinaigrette | Lean protein, vitamins, and minerals |
| Snack | Greek yogurt with fruit | Protein and calcium |
| Dinner | One slice of cheese pizza (whole-wheat crust preferred) with a side salad | Moderate calories, carbohydrates, and some protein and fat |
| Snack (optional) | Small piece of fruit | Vitamins and natural sugars |
Serving Size and Dietary Recommendations

Determining appropriate serving sizes for cheese pizza depends heavily on individual dietary needs, caloric goals, and overall eating patterns. A standardized serving size is not universally applicable due to the significant variations in pizza size, crust thickness, and cheese quantity across different brands and homemade preparations. Understanding these variables is crucial for making informed choices about pizza consumption.Appropriate serving sizes should be considered within the context of a balanced diet.
For example, a single slice from a large, commercially prepared pizza might represent a substantial portion of one’s daily caloric intake, potentially exceeding recommended limits for saturated fat and sodium. Conversely, a smaller, thinner-crust pizza made with whole wheat flour and reduced-fat cheese could offer a more nutritionally balanced option, even when consumed in larger quantities.
Serving Size Recommendations Based on Dietary Needs and Caloric Goals
The recommended serving size for cheese pizza varies significantly depending on individual caloric needs and health goals. A person aiming for weight loss might opt for a single, smaller slice (approximately 1/6th to 1/8th of a large pizza), whereas someone with higher caloric needs might consume two or more slices, depending on their overall daily intake. It’s crucial to consult a registered dietitian or nutritionist to determine personalized serving sizes based on individual factors like age, activity level, and health conditions.
For instance, a highly active individual may be able to incorporate a larger serving size of pizza into their diet without negatively impacting their weight management goals, compared to a sedentary individual. Tracking caloric intake using a food diary or mobile application can also assist in making informed decisions about portion control.
Incorporating Cheese Pizza into a Weight Management Plan
Including cheese pizza in a weight management plan requires mindful consideration of portion control and overall dietary balance. Substituting a high-calorie, high-fat commercial pizza with a homemade version using whole-wheat crust, reduced-fat cheese, and plenty of vegetables can significantly reduce the overall caloric and fat content. Moreover, opting for smaller slices or sharing a pizza with others can contribute to weight management.
For example, instead of consuming an entire large pizza, choosing a smaller personal-sized pizza or sharing a large one with friends or family can help control portion sizes and reduce overall caloric intake. Furthermore, incorporating regular physical activity alongside a balanced diet, including occasional treats like pizza, can promote successful and sustainable weight management.
Nutritional Differences Between Homemade and Commercially Prepared Cheese Pizzas
Homemade and commercially prepared cheese pizzas can differ significantly in nutritional content. Homemade pizzas generally offer greater control over ingredients, allowing for healthier substitutions. For example, using whole-wheat flour for the crust increases fiber content, while opting for low-fat cheese reduces saturated fat. Additionally, adding plenty of vegetables significantly enhances the nutritional value, boosting vitamin and mineral intake. Conversely, commercially prepared pizzas often contain higher levels of sodium, saturated fat, and refined carbohydrates.
Many commercial brands utilize processed ingredients and preservatives, which can negatively impact nutritional value. For instance, a comparison of a typical large commercial pepperoni pizza versus a homemade vegetable pizza with whole-wheat crust and low-fat mozzarella reveals a stark difference in sodium, fat, and fiber content, with the homemade option often providing significantly more fiber and fewer unhealthy fats.
This highlights the importance of making informed choices regarding pizza preparation methods.
FAQ Compilation: Cheese Pizza Nutrition Facts
Is cheese pizza a good source of calcium?
Yes, the cheese in pizza provides a significant amount of calcium, an essential mineral for bone health.
Does the type of crust significantly impact the nutritional value?
Yes, thin crust pizzas generally have fewer calories and carbohydrates compared to deep-dish or thick crust options.
Are there healthier topping options for cheese pizza?
Definitely! Adding vegetables like mushrooms, peppers, or onions increases the fiber and vitamin content, while lean meats like chicken breast offer additional protein.
How often can I eat cheese pizza without negatively impacting my health?
Occasional enjoyment is fine. Regular consumption, however, may lead to excessive sodium and saturated fat intake, so moderation is crucial.
